Rubber Elastomer Properties
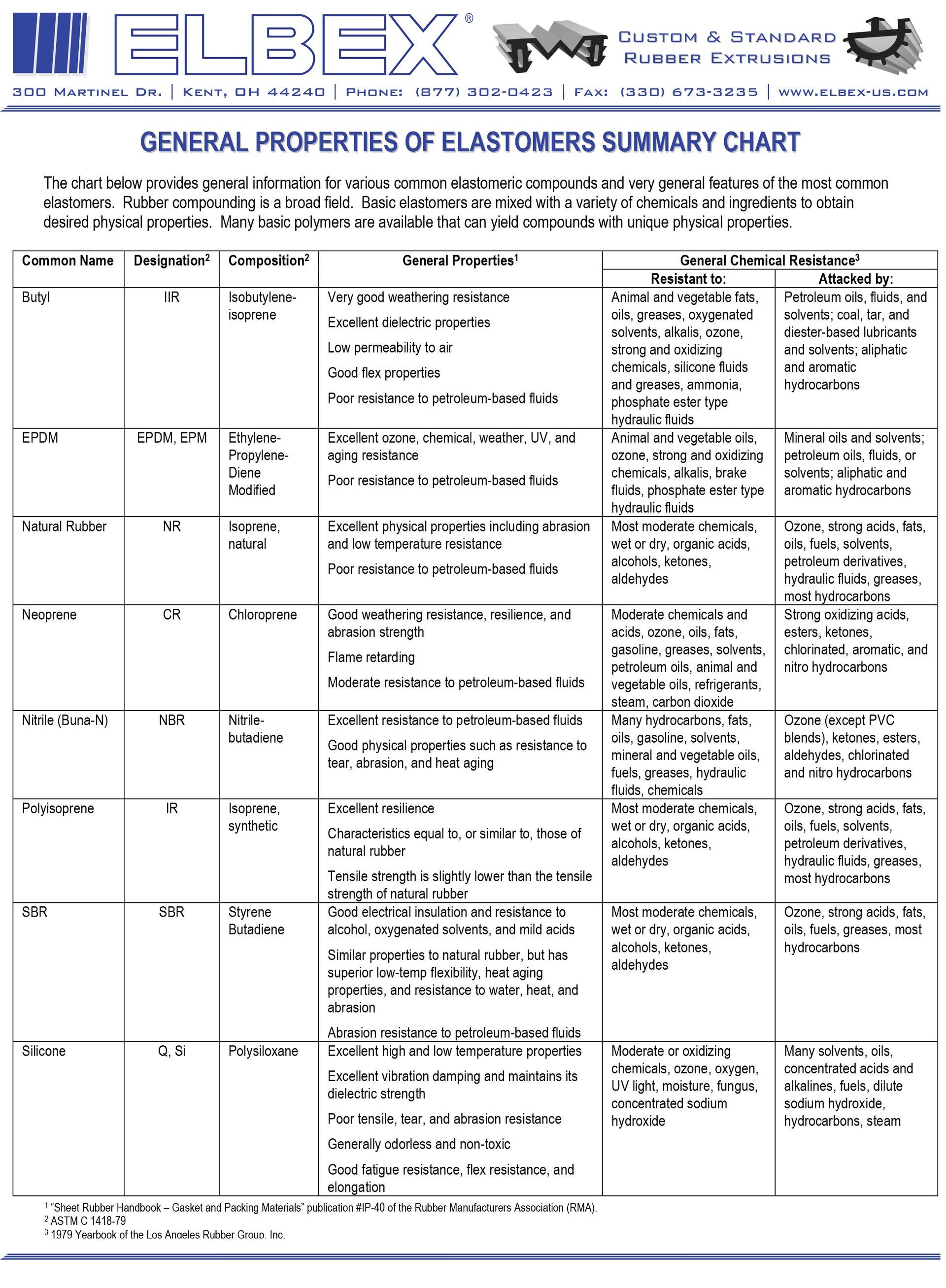
The rubber properties chart below provides general information for various common elastomeric compounds and very general features of the most common elastomers. Rubber compounding is a broad field. Basic elastomers are mixed with a variety of chemicals and ingredients to obtain desired physical properties. Many basic polymers are available that can yield compounds with unique physical properties.
The rubber properties chart below provides
- General information for various common elastomeric compounds and
- General features of the most common elastomers.
Rubber compounding is a broad field. Basic elastomers are mixed with a variety of chemicals and ingredients to obtain desired physical properties. Many basic polymers are available that can yield compounds with unique physical properties.
Contact Us for additional rubber extrusions information, or send us your custom rubber extrusion profile requirements.
Engineering Resources to
Support Your Project
ELBEX Corporation is committed to providing top-notch support to its customers during the design and manufacturing process. We understand that the success of our clients is directly tied to our ability to provide them with the highest level of service possible. Therefore, we work closely with our customers to ensure that their needs are fully understood and met. Our team of experts has a wealth of experience in the industry, which enables us to provide valuable insights and advice to our clients.
CUSTOM ON-SITE TOOLING
We meet our customers’ needs for unique custom extrusions with in-house, custom tool and die design services.
TECHNICAL RESOURCES
We offer several technical resources and PDFs to assist in the design of effective and efficient rubber extrusions.
DESIGN ASSISTANCE
We evaluate your unique application need and are prepared to offer design assistance and troubleshoot previous issues as needed.











