What is SBR?
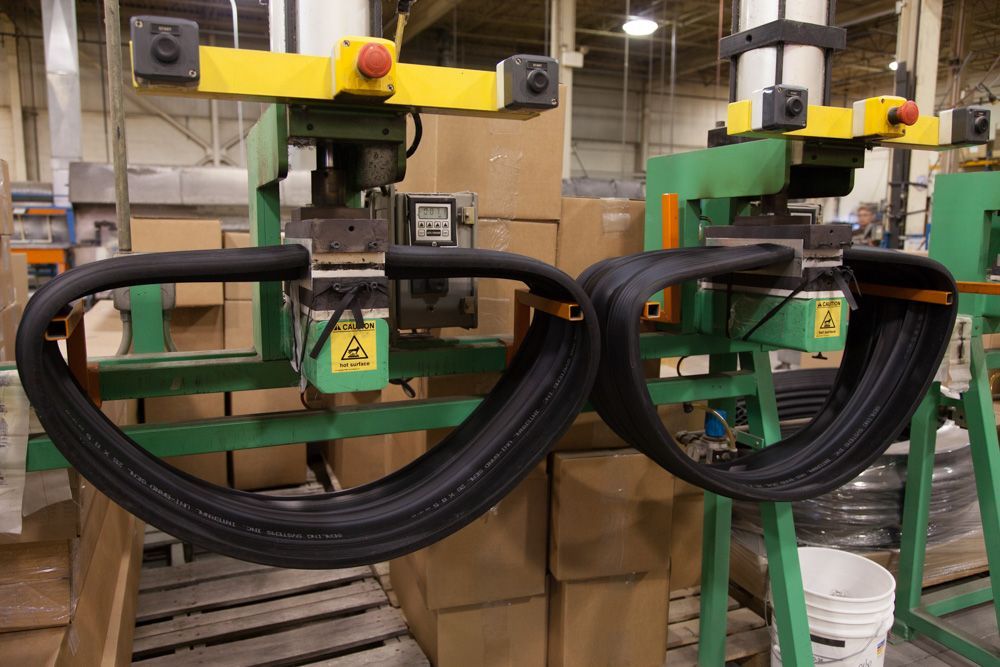
SBR, also known as BunaS, is a synthetic copolymer of styrene and butadiene. SBR was originally developed to replace natural rubber in tires and its use in the manufacture of tires continues to the present day. SBR and natural rubber account for 90% of the total world rubber consumption.
SBR has a typical service temperature range between –50° F and +225° F.
ADVANTAGES:
SBR has similar properties to natural rubber, but SBR has superior water resistance, heat resistance, abrasion resistance, low temperature flexibility, and heat aging properties (i.e., in excess heat SBR hardens and becomes brittle instead of softening like natural rubber does). SBR also has good electrical insulation, alcohol resistance, oxygenated solvent resistance, and mild acid resistance. SBR can be successfully bonded to a wide range of materials.
LIMITATIONS:
SBR has poor resistance to oils, fuels, hydraulic fluids, strong acids, greases, fat, and most hydrocarbons. Without special additives, SBR is vulnerable to ozone, oxygen and sunlight.
COMMON APPLICATIONS:
SBR is recommended for applications where water, automotive brake fluid, or alcohols with a low molecular weight are present. Common applications include tire, tubes, gaskets, belts, hoses, seals, shock mounts, skirt board rubber, lining rubber, and conveyor belt covers. SBR is not normally produced in o-ring form.
Durometer
The hardness of rubber compounds is measured by the Shore A durometer; the higher the durometer number, the harder the compound. Softer compounds stretch easier and seal better on rough surfaces. Harder compounds offer greater abrasion/extrusion resistance.
Typical Questions Asked
- What is the application or function of the part?
- Is there a target cost per part that should be considered?
- Will the part be located inside or outside?
- What, if any, are the temperature requirements?
- Is there exposure to specific chemicals?
- Does the part need to meet any regulatory requirements?
Now that you know what materials your project needs, fill out a request for a quote form to get started.
For more detailed information on material selection, please see our engineering technical information page. Several PDF data sheets are available for download.
Engineering Resources to
Support Your Project
ELBEX Corporation is committed to providing top-notch support to its customers during the design and manufacturing process. We understand that the success of our clients is directly tied to our ability to provide them with the highest level of service possible. Therefore, we work closely with our customers to ensure that their needs are fully understood and met. Our team of experts has a wealth of experience in the industry, which enables us to provide valuable insights and advice to our clients.
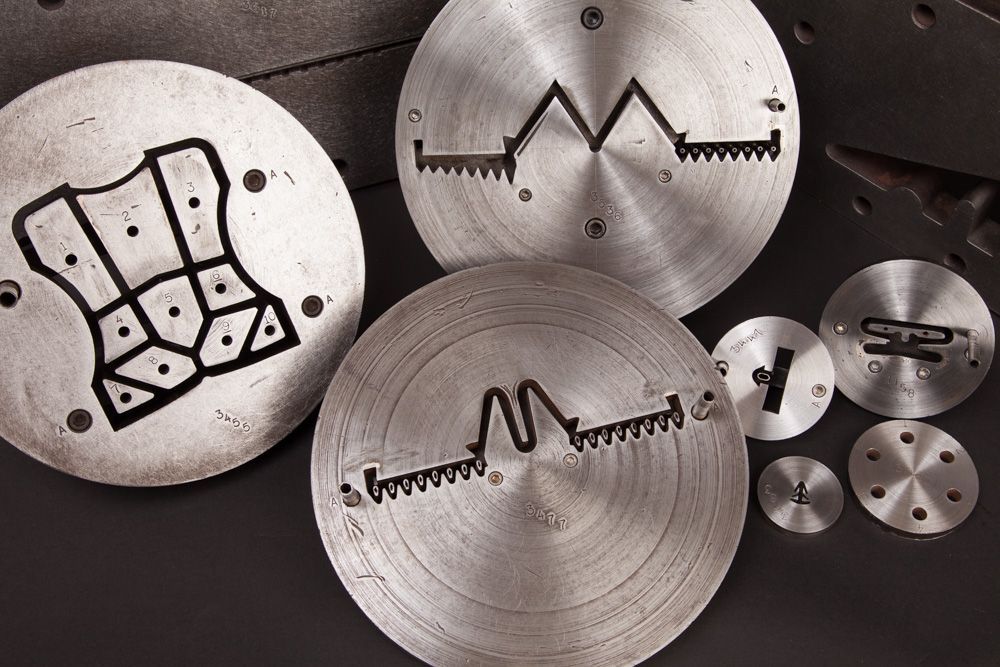
CUSTOM ON-SITE TOOLING
We meet your needs for custom extrusions with in-house, custom tool and die design services.
TECHNICAL RESOURCES
Find technical resources and to assist in the design of effective and efficient rubber extrusions.
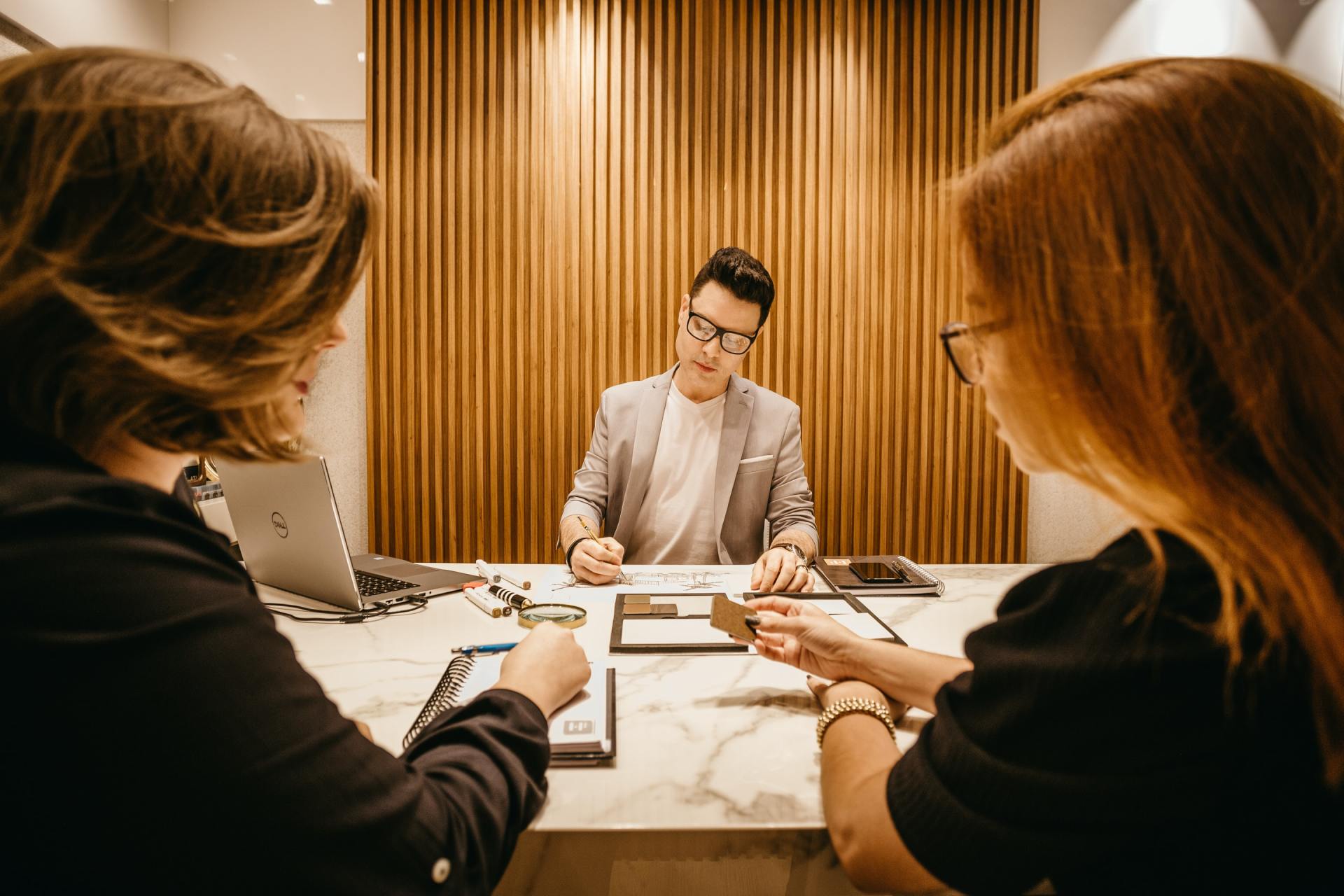
DESIGN ASSISTANCE
We're ready to offer design assistance and troubleshoot old problems for your unique project.